"AILING AIRPORTS IN PANDEMIC" - Leaving No Bags Unattended
- Yashasvi Sharma
- Jul 1, 2020
- 4 min read
In the recent event of “COVID-19” we are witnessing the stagnation of flights worldwide. The scenario is nowhere at a point of improvement but degrading day by day. In the times when most of these flights are not operating except emergency ones, it is not only difficult for the airlines, but also difficult for the airports to manage themselves as an independent identity.
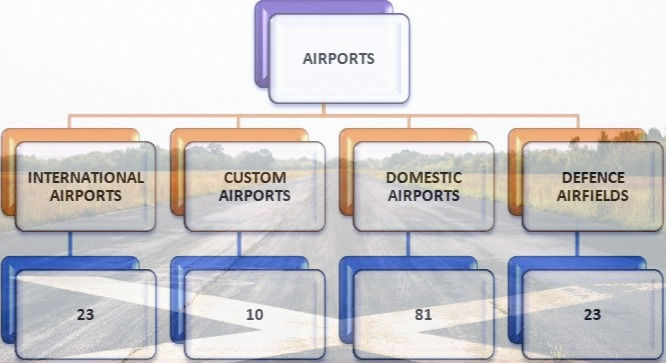
From Indira Gandhi International Airport, New Delhi, Situated in the capital as one of the world's busiest airports to the world's most challenging airports at Leh & Ladakh, Sikkim, Lakshadweep Island India has a fleet of more than 137 Airports in including International, custom, domestic & defense.
For further instances the government is focusing on more FDI (foreign direct Investment) in the airport sector. Over the past few years it is clearly visible that the number of people travelling through flights are increasing on a yearly basis. Hence, the government is following an aggressive strategy in developing more airports across the country.
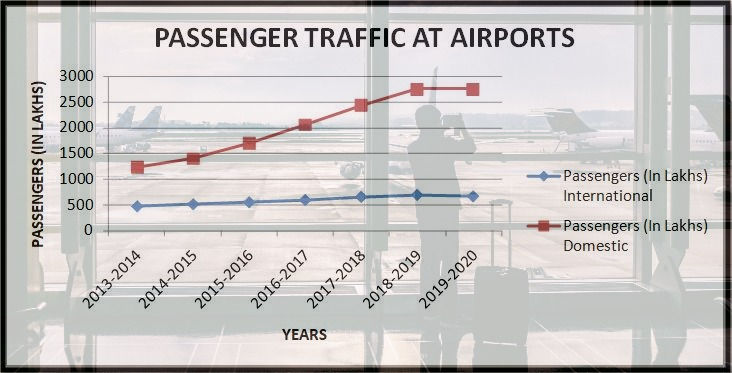
India is witnessing a outbreak in domestic travelling reaching an all time high. If we see the trends from 2013 to 2020 we can see that domestic travelling is witnessing a average increase of 15%, on the other hand international travelling is close to 6%.
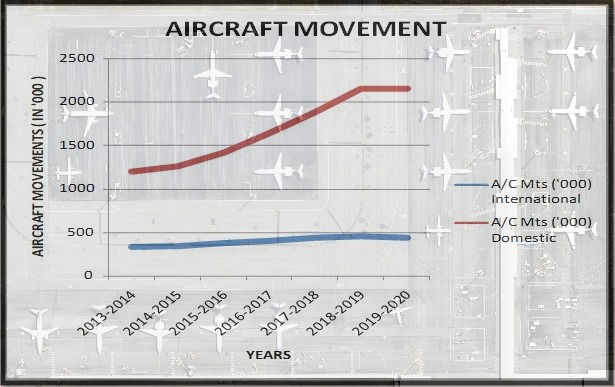
In support of this, we can also see that domestic aircraft movement is growing at an average pace of 10% in comparison to the international growth of 4%. All these factors clearly point out to a scenario where increase in domestic traffic at the airports over the recent period of time calls for more investment in this sector.
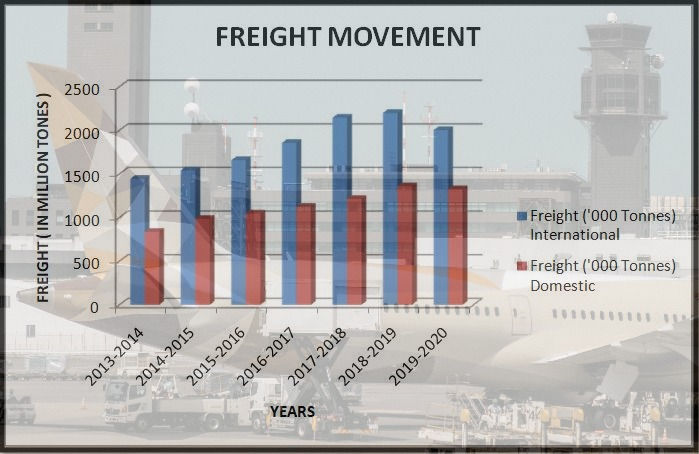
On the contrary we can see that when the movement of freight is concerned, International movement overtakes the domestic one but as far as the growth rate is concerned, it is at an average pace of 8% for domestic & 6% for international. It clearly shows that not only for passenger movements but freight movement is also increasing at a rapid pace. All the above three discussed parameters are shaken badly in the pandemic. The situation is such that now the focus is on survival rather than the growth in the airport sector. Although, government in its recent decision decided to lease out 6 airports namely Ahmedabad, Jaipur, Lucknow, Guwahati, Thiruvananthapuram and Mangaluru for PPP model (Public Private Partnership). As per government, “The airport sector is the top contender among infrastructure sectors in terms of international interest. International operators and investors prefer brownfield airport expansion opportunities with having more than 3-4 million passenger capacity. The airport sector may provide an immediate opportunity to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) by adoption of a PPP approach”.

To continue this pace the government also announced 6 more new airports for PPP models under the “Atmanirbhar Bharat Mission” & these 12 airports will bring an investment of Rs. 13,000 crore for job creation & infrastructure development.
But, the major concern is the current scenario when the number of flights operating are very less. In order to understand this question of why the number of flights operating & passengers travelling affect the airport we have to look into the revenue side & expenditure side for an airport.
Firstly, the revenue side comprises more than 70% of revenue is directly linked with the flights operating & passengers movement, which is expected to see a steep downside in this lock down.
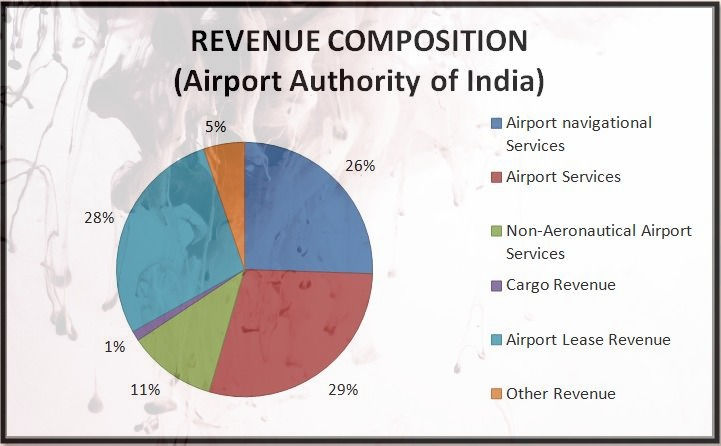
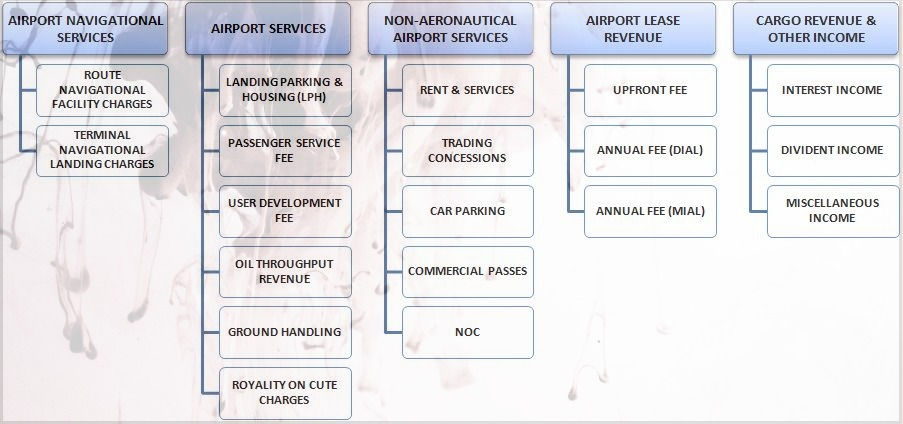
ROUTE NAVIGATION FACILITY CHARGES (RNFC) - These Charges are levied for providing air navigation services to aircraft for landing, overflying etc. They are charged on the basis of weight cum distance formula. For example an aircraft flying from Australia to Dubai over Indian Airspace & it was using Indian ground Navigation aids,So Australian Airline has to pay RNFC for the service rendered by Indian ATC.
TERMINAL NAVIGATIONAL LANDING CHARGES (RNFC)- These Charges are levied for providing landing services to aircraft for landing. The are charged on the basis of weight of aircraft.
HOUSING CHARGES- Housing charges are to be levied when aircraft is parked in the hanger owned by AAI.
PARKING CHARGES- Parking charges are to be levied for parking of aircraft in open/in contact stands.
PASSENGER SERVICE FEE- It includes facilitation & security charges for passenger.
USER DEVELOPMENT FEE - It is a charge levied by airports on passengers to recoup the investment & development work such as the building of a new terminal building or a new runway.
CUTE FEE- It stands for 'Common User Terminal Equipment' and is actually charged by the Airport Authority of India for the customer's use of metal detecting machines, escalators and other equipment.
DIAL/MIAL- Delhi International Airport Limited (DIAL) and Mumbai International Airport Limited (MIAL) had set up a Marketing Fund in April 2010 and August 2012 respectively to collect 0.5 per cent and one per cent, respectively, of net sales from various concessionaires as a marketing fund charge to “promote business” at the two airports.
OIL THROUGHPUT REVENUE- It is the fee paid by fuel supplier to the airport authority, currently govt. has discontinued this.
TRADING CONCESSIONS- Revenue from various businesses across the airport.
On the other hand as far as the expenditure is concerned more than 50% of the expenditure is of recurring nature & can be considered fixed with less amount of variability.
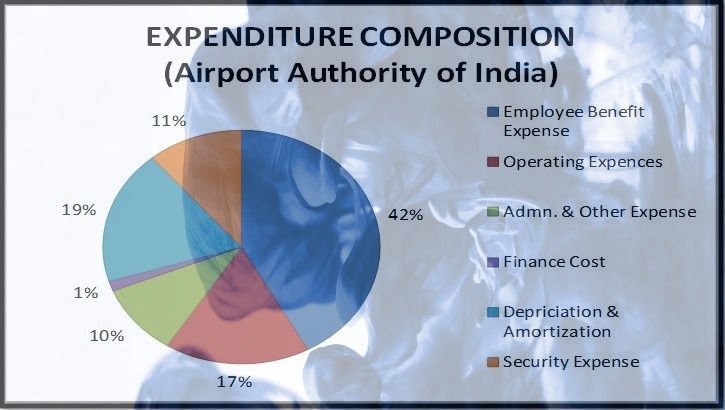
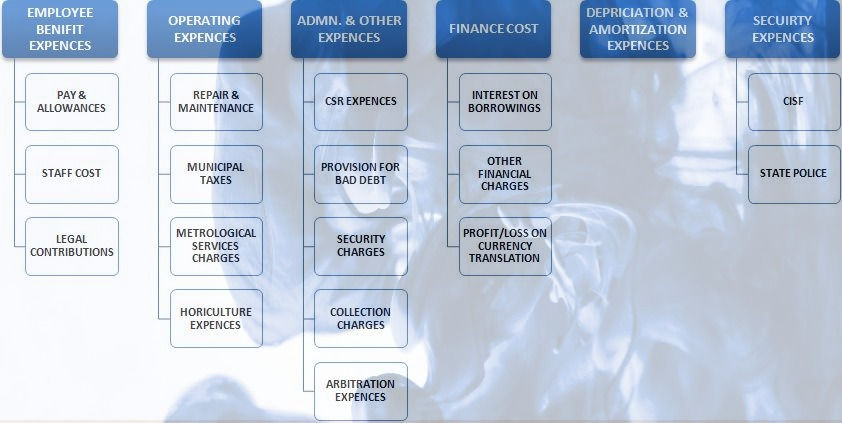
In order to come out through these tough times & maintain a decent amount of break even it is required to either increase revenue in comparison to expenditure or to reduce expenditure against same level of revenue. But in a scenario where revenue decreases suddenly & cost remains more or less the same it is expected to be a loss making scenario. In order to deal with it the only option is cost effectiveness. Ultimately airports will increase various charges to be charged from airlines in order to ensure their profitability & airlines will recover the same from customer which will show a potential increase in the ticket prices.
The recent time of COVID-19 on a positive note has shown us the way of survival while reducing the expenditure & not reducing jobs. Only the companies, organizations, institutions who work effectively & efficiently can survive in the long run.


Comments